


- Vascular Thrombosis
-
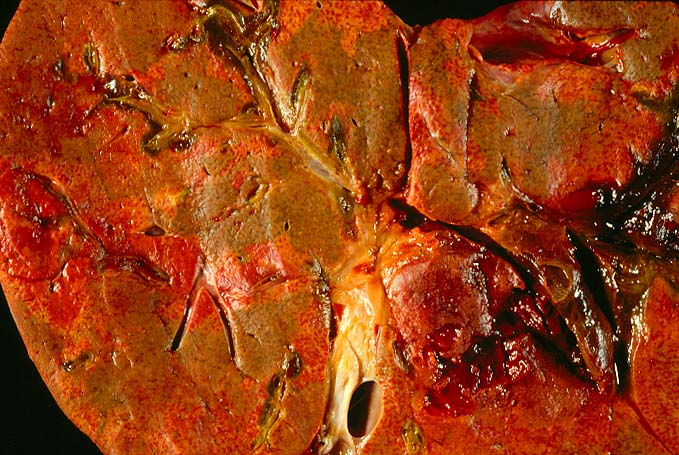
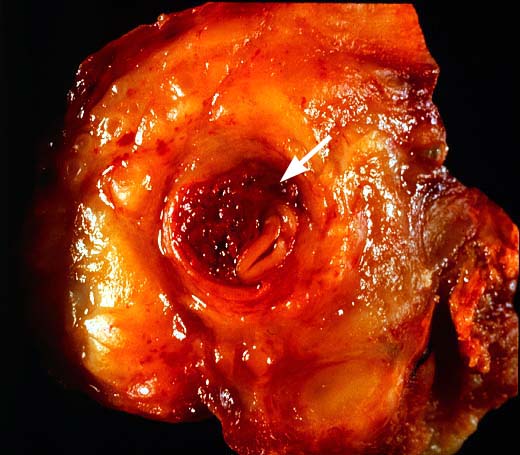
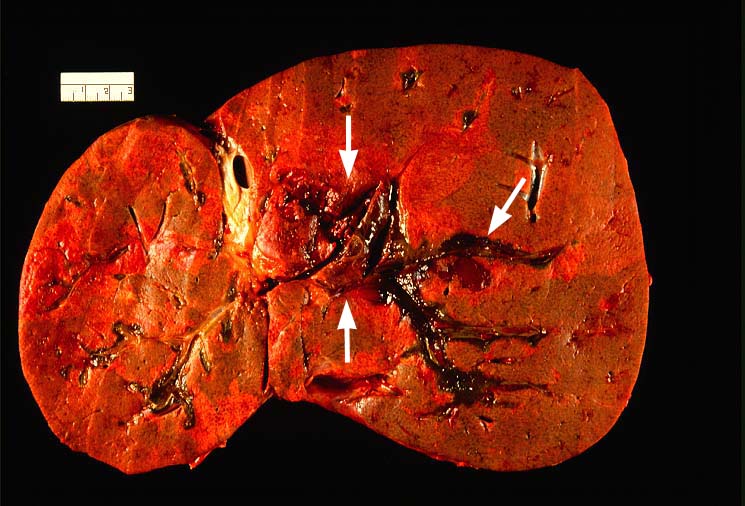
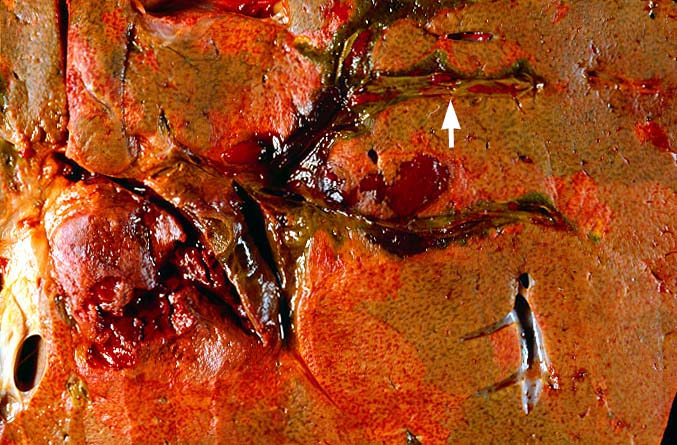
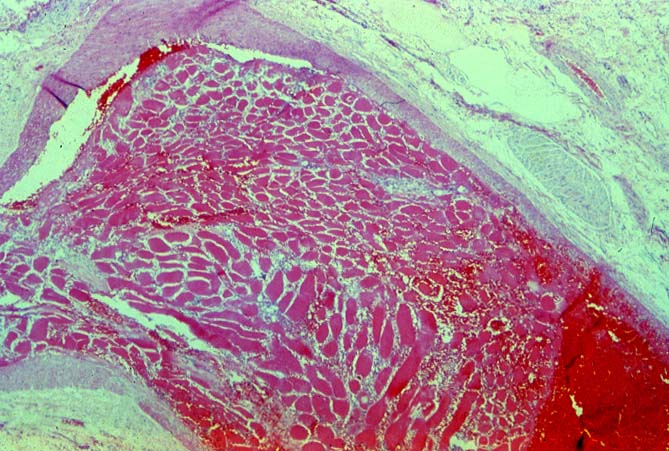
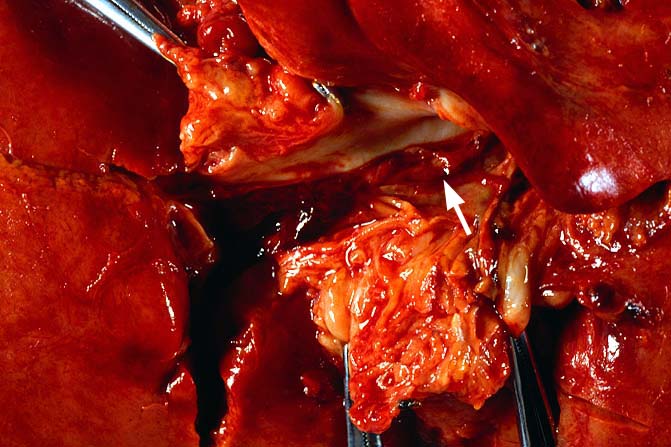
Vascular thrombosis is probably the most serious post-transplantation
technical complication and most often involves the hepatic arterial
system. Thrombosis of the portal or hepatic veins or vena cava are
much less common. Arterial thrombosis most frequently occurs during
the first several weeks after transplantation, with a later and smaller
increase occurring 1 - 3 years after transplantation. The clinical
manifestations depend on the time after transplantation, which in turn,
determines whether arterial collateral circulation has had time to
develop. Therefore, the clinical presentation may vary from acute
hepatic failure to relapsing febrile episodes or be completely
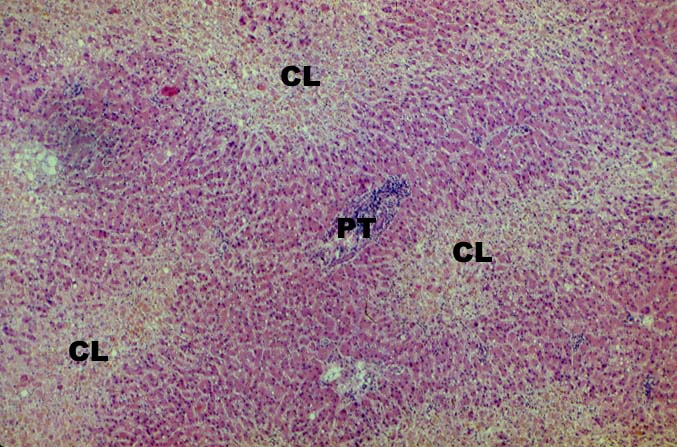
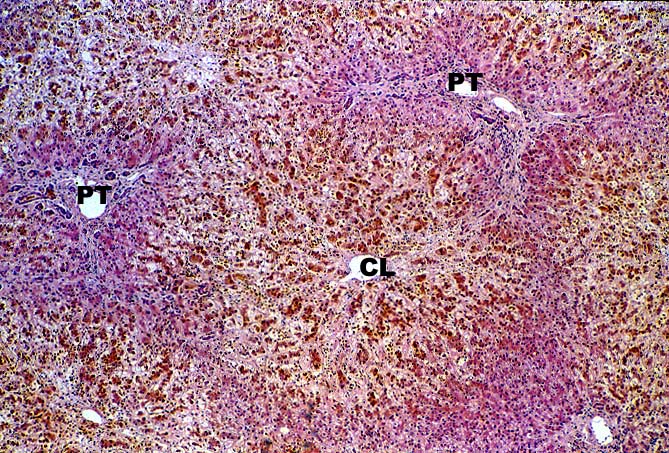
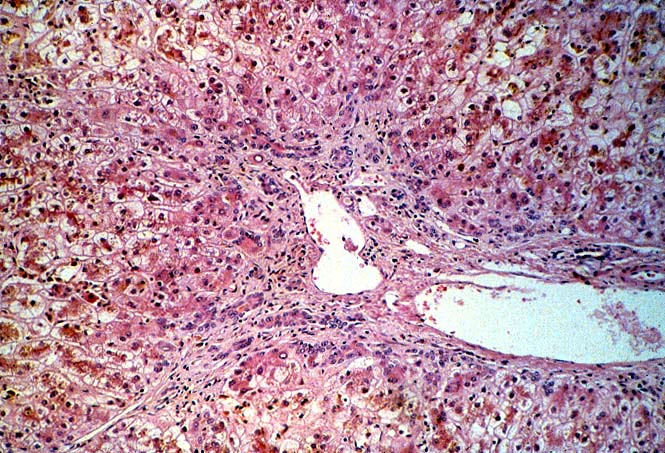
asymptomatic. It is important to remember however, that the hepatic
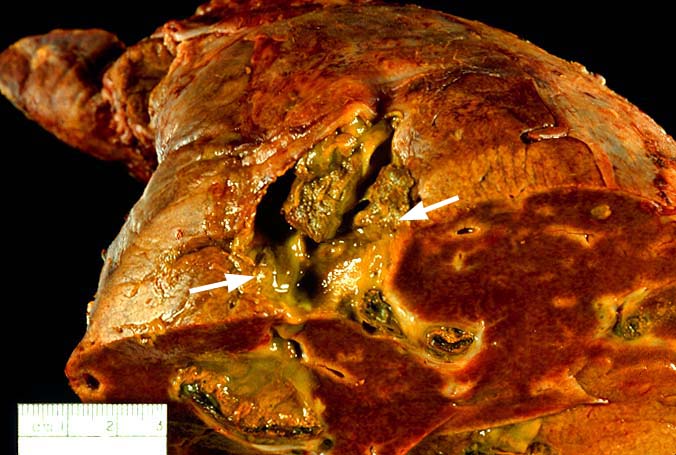
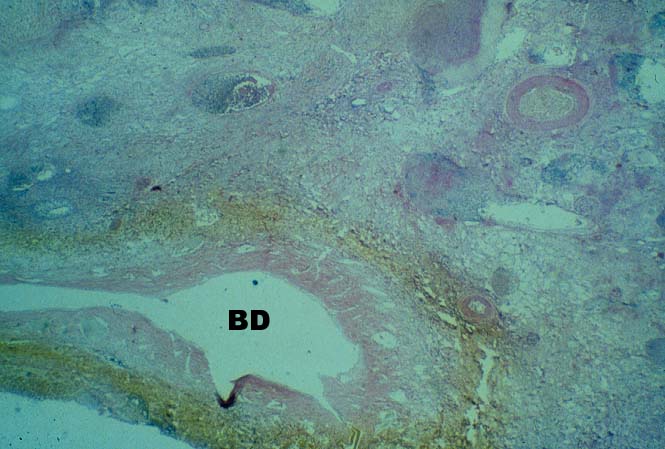
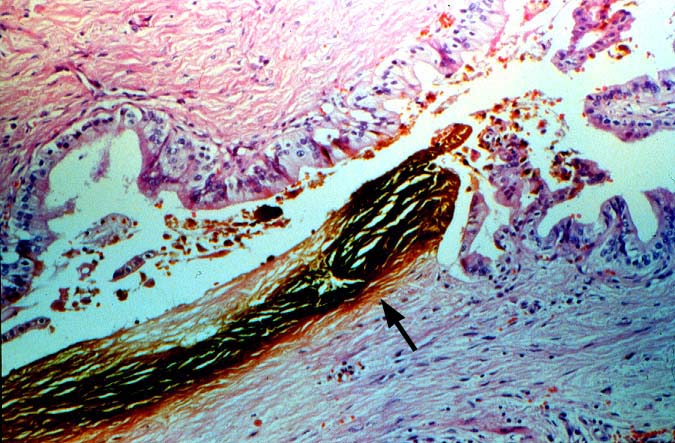
artery is the sole source blood supply to the biliary tree and
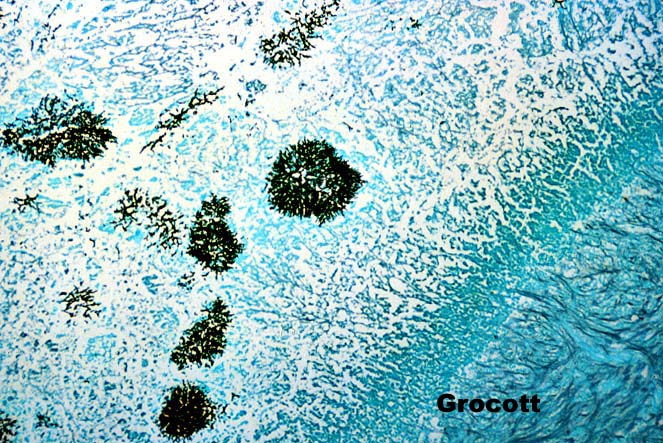
arterial thrombosis frequently results in necrosis of bile ducts.
This can cause biliary leaks, sludge and/or obstruction. Therefore,
any time biliary tract pathology is seen in a liver allograft, one
should think of arterial insufficiency.
Please mail comments, corrections or suggestions to the
TPIS administration at the UPMC.
[FRAMES]
[NO FRAMES]












