 |
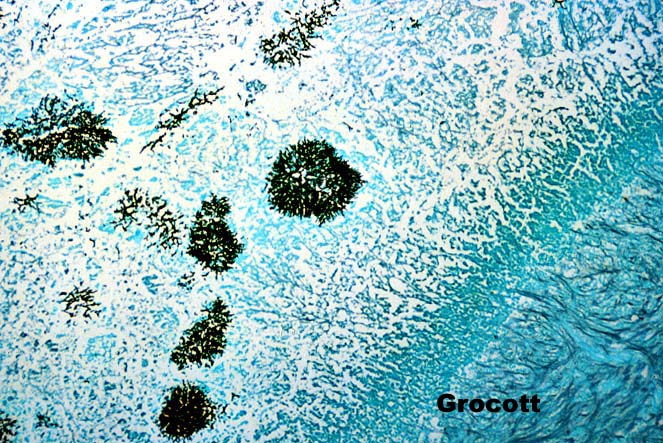
| Figure 8. Hepatic artery thrombosis, particularly within the first few weeks after liver transplantation when the allograft is devoid of collateral arterial circulation, results in necrosis of the large bile ducts. The necrotic tissue, particularly in and around the biliary tree, is fertile soil for the growth of fungi and bacteria. When such tisue is encountered, a gram and grocott stain should be routinely examined. This photomicrograph of a Grocott(Methenamine silver stain) highlights the pseudohyphae, typical of Candida infection, which invade a necrotic bile duct after hepatic artery thrombosis. |