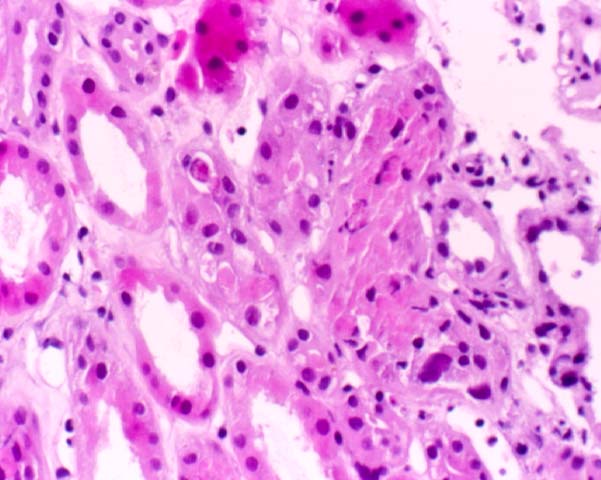
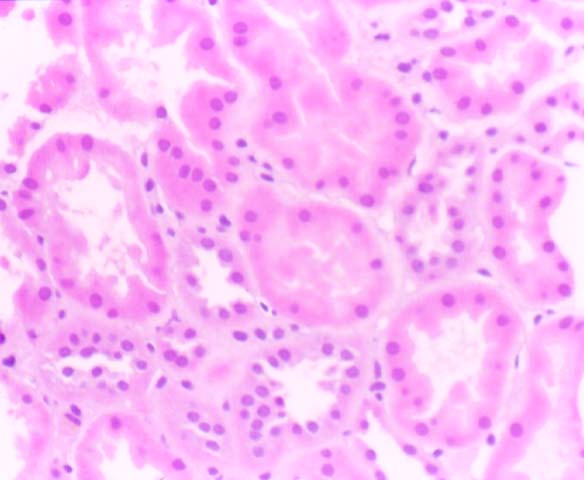
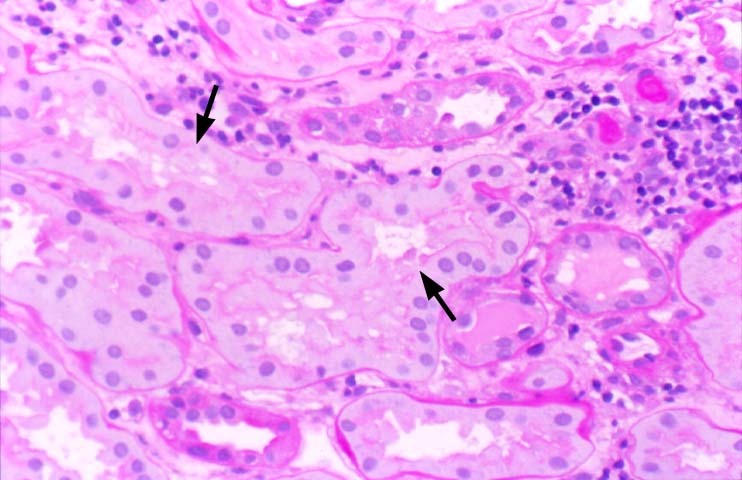
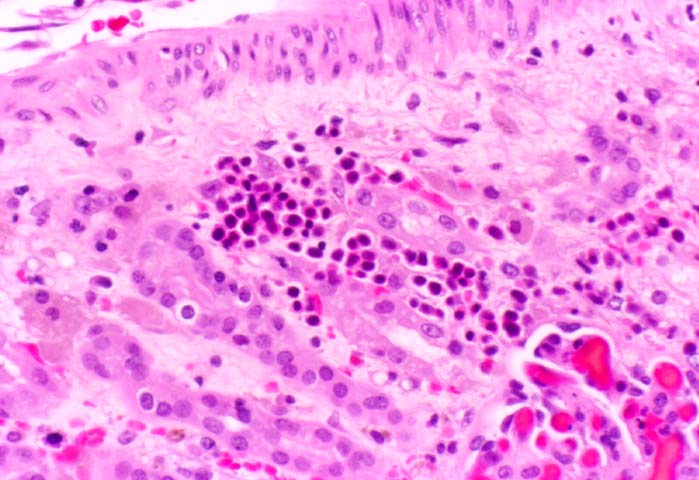
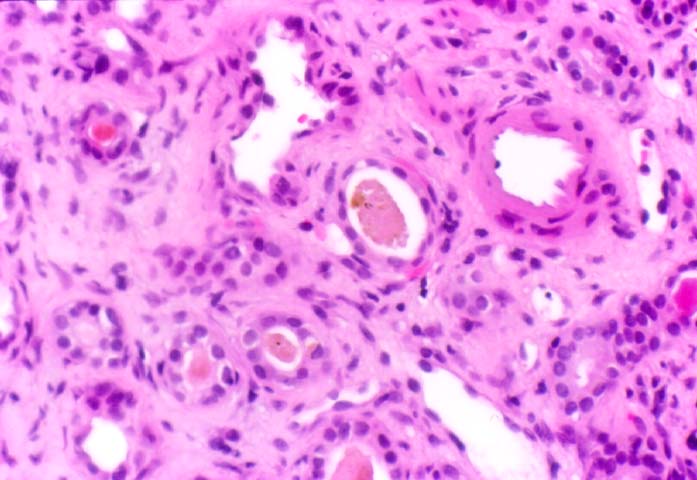
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Ischemic injury to the donor organ during harvesting and subsequent transplantation into the patient, is a common cause of oliguria/anuria in the immediate post-transplant period. The clinical course is usually self-limited, and recovery ensues within a few weeks. Biopsies of the allograft during the ischemic phase show coarse irregular cytoplasmic vacuoles in the renal tubular epithelium and focal coagulative necrosis. During the resolution phase of the injury, the tubules may only show non-specific dilatation, cast formation, and regeneration. The peri-tubular capillaries sometimes show extra-medullary hematopoiesis. In the glomeruli, severe ischemic injury may result in capillary thrombi and neutrophilic infiltration.
References
|
|
|
|