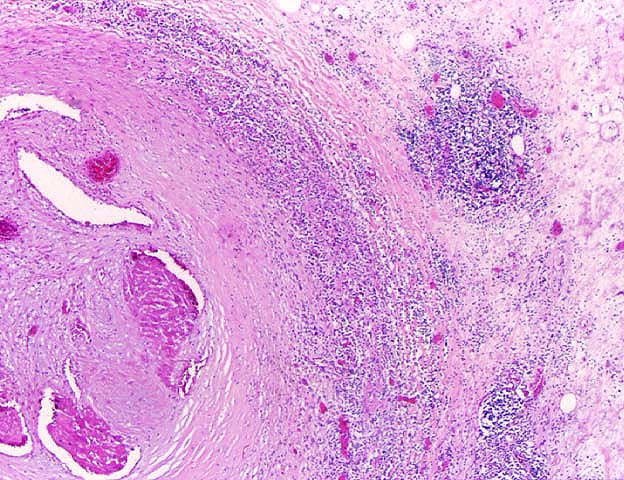
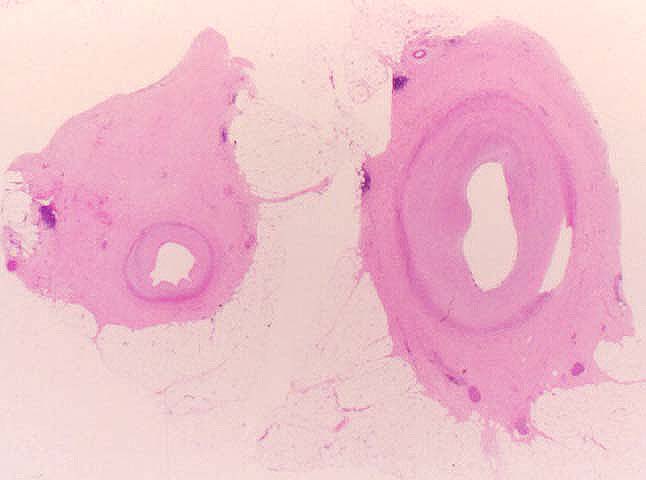
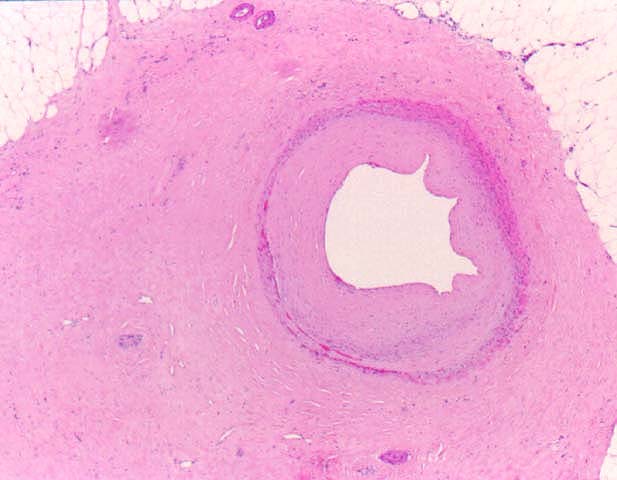
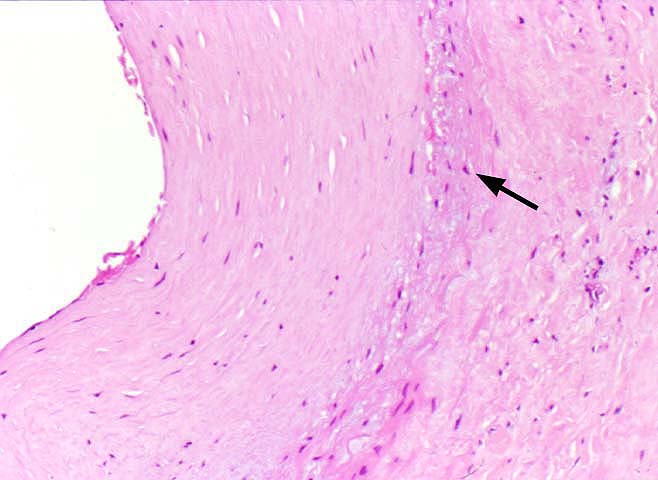
Chronic rejection is the single most significant obstacle to long
term organ allograft survival. It similar manifests in all vascularized
solid organ allografts as obliterative arteriopathy or graft vascular
disease(GVD), interstitial fibrosis and atrophy of parenchymal
elements that eventually result in allograft failure. Chronic
rejection usually has an insidious onset, although abrupt arterial
damage from a severe acute rejection can manifest similar arterial
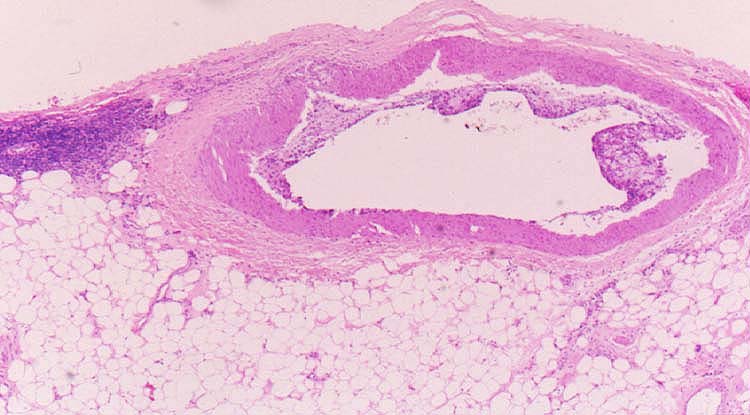
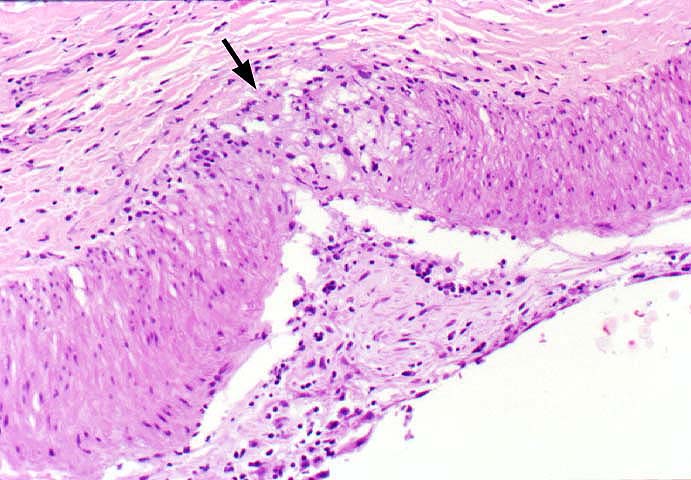
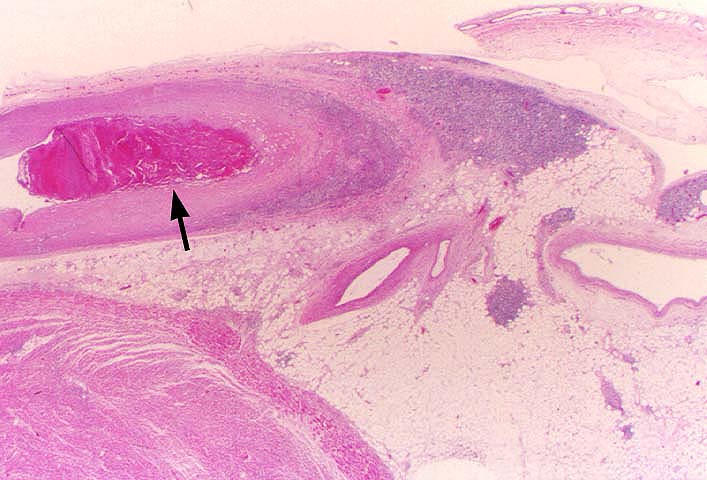
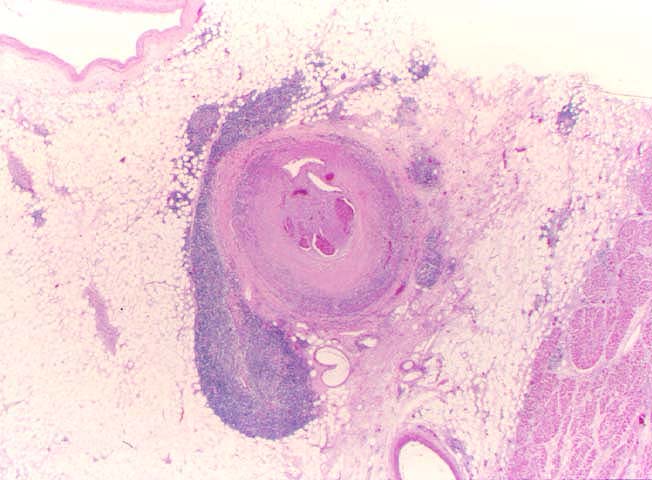
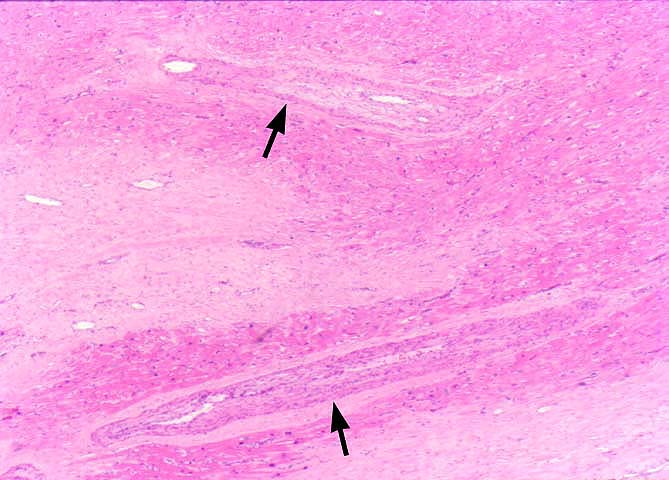
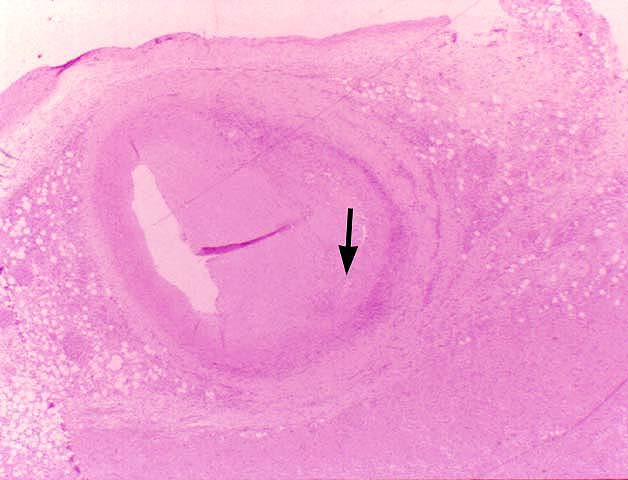
pathology. The principal histopathological finding in GVD is
concentric narrowing of the arterial lumen because of fibrointimal
hyperplasia. Veins are much less frequently and less severely
involved.
Although GVD or OA is similar to atherosclerosis seen in the
general population, there also are distinct differences. A comparison
of the two is shown below:
Table 1. Comparison of GVD and atherosclerosis in
the general population.
| Histopathological Finding | Graft
Vascular Disease
| Atherosclerosis |
| Epicardial Coronary arteries | Involved
| Preferentially involved |
| Penetrating intra-myocardial arteries | Involved
| Not involved |
| Endothelium | Often intact, but hypertrophied
| Usually intact, hypertrophy not as obvious as GVD
|
| Myointimal proliferation and lumenal narrowing
| Yes, concentric | Yes, eccentric
|
| Intimal lipid and cholesterol deposits |
Uncommon | Common |
| Intimal inflammation | Variable
| Variable |
| Elastic lamina | Focally disrupted
| Focally disrupted |
| Media | Thinned in late stage
| Thinned in late stage |
| Medial inflammation | Variable
| Variable |
| Adventitial Inflammation | Common
| Variable |
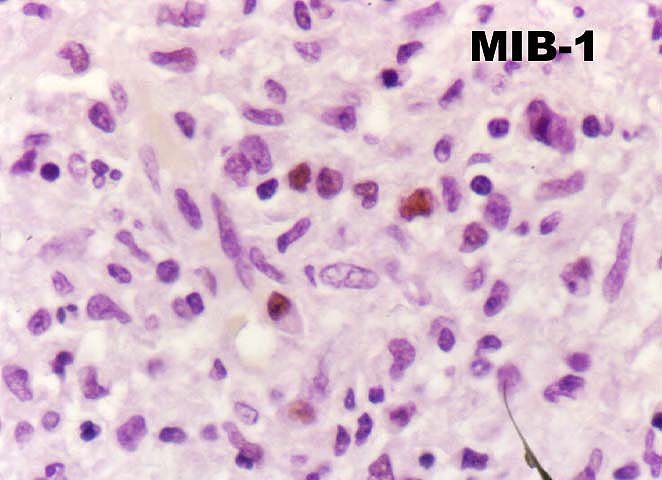
GVD is thought to be due to direct immunological injury to the
allogeneic arterial endothelium, which disrupts intimal homeostasis.
In turn, the injury is thought to trigger a cytokine and growth-factor-driven
arterial repair response that results in lumenal narrowing. Several
excellent reviews of this subject of this subject are suggested
(1-7).
Selected References
- Hayry P, Isoniemi H, Yilmaz S, et al. Chronic allograft rejection.
Immunol Rev 1993;134:33-81.
- Adams DH, Russell ME, Hancock WW, et al.
Chronic rejection in experimental cardiac transplantation: studies in the
Lewis-F344 model. [Review]. Immunol Rev 1993;134:5-19.
- Billingham ME. - Pathology and etiology of chronic rejection of the heart.
Clin Transplant 1994;8(3 Pt 2): 289-292.
- Demetris AJ, Zerbe T, Banner B. Morphology of solid organ allograft
arteriopathy: identification of proliferating intimal cell populations.
Transplant Proc 1989;21(4):3667-3669.
- Ewel CH, Foegh ML. - Chronic graft rejection: accelerated transplant
arteriosclerosis. [Review]. Immunol Rev 1993;134:21-31.
- Paul LC, Davidoff A, Benediktsson H. Cardiac allograft atherosclerosis in
the rat. The effect of histocompatibility factors, cyclosporine, and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Transplantation 1994;57(12):1767-1772.
- Matas AJ, Burke JF, Jr., DeVault GA, Jr., Monaco A, Pirsch JD. - Chronic
rejection. [Review]. J Am Soc Nephrol
1994;4(8 Suppl): S23-S29.