Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None.
TPIS Related Resources:
Kidney
Transplant Topics
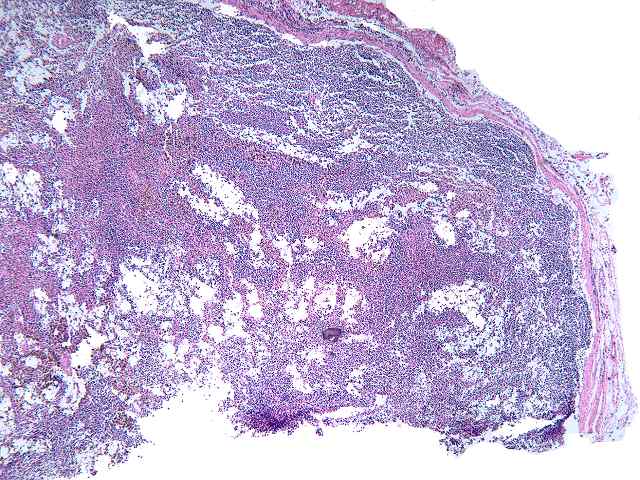
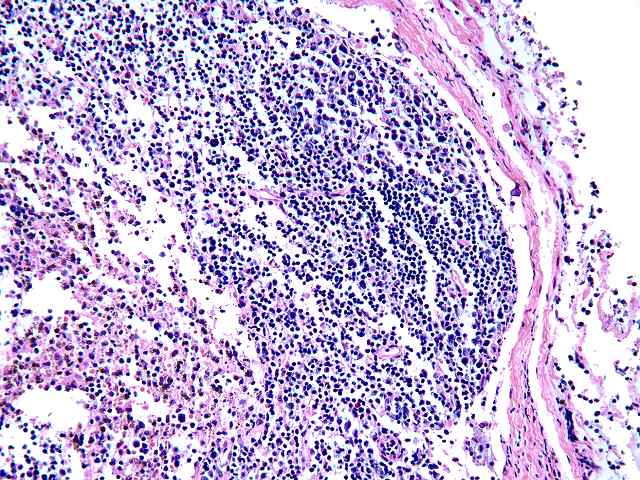
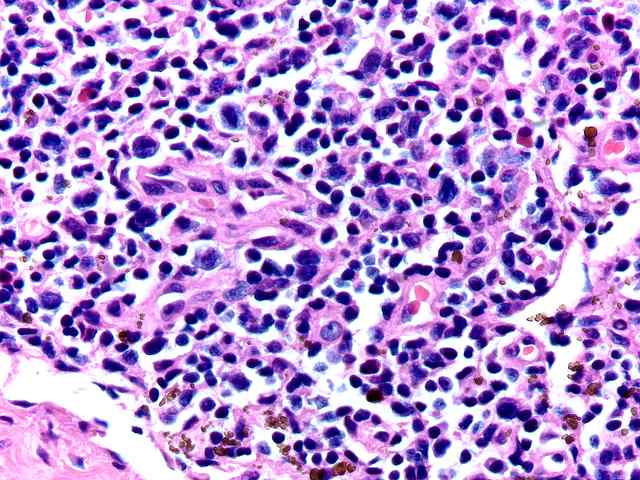
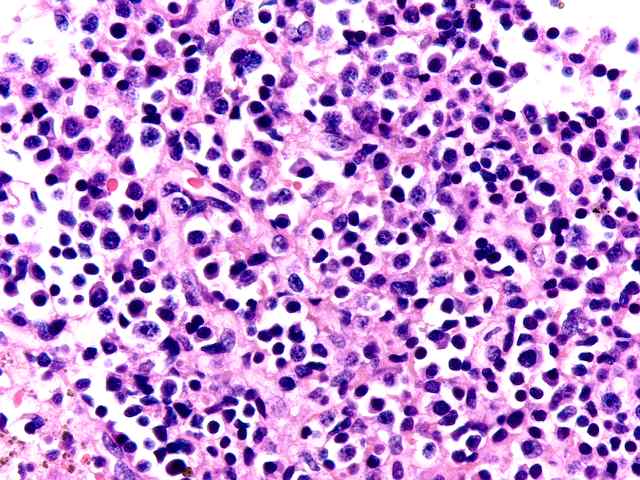
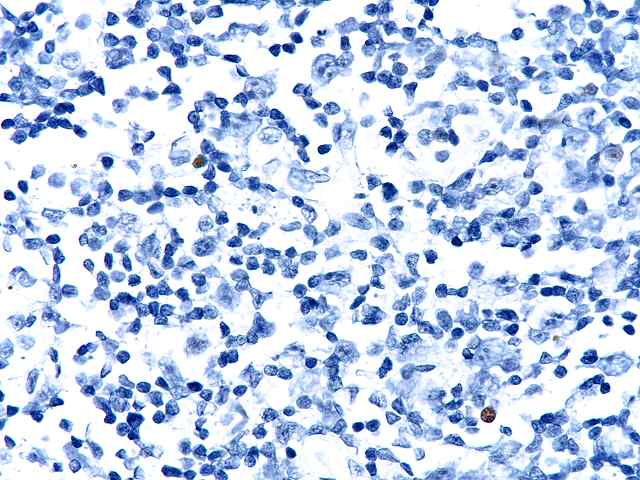
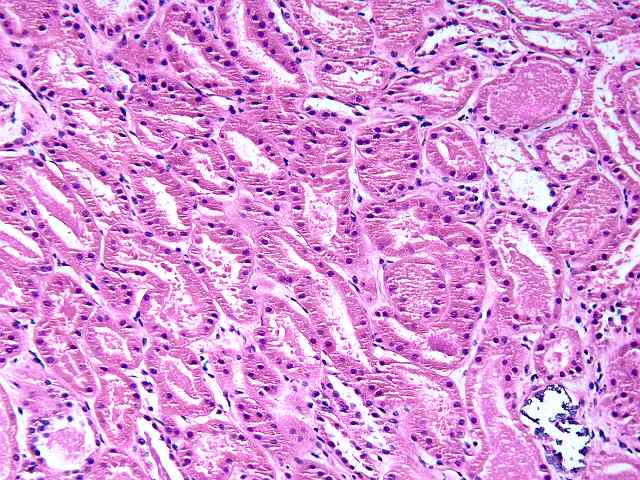
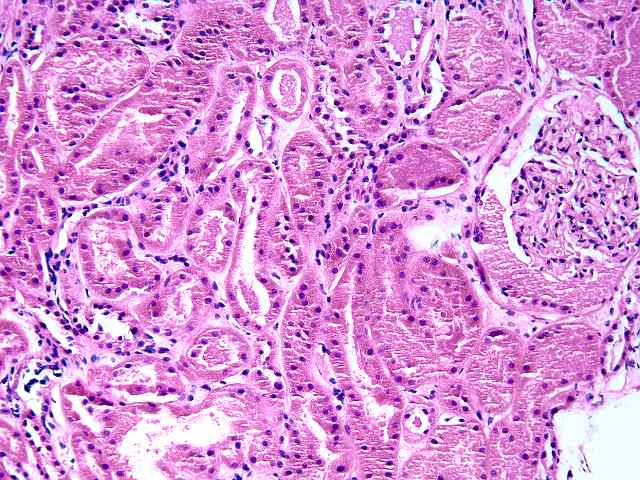
The specimen consists of two slides, one containing lymph nodes, and one a renal biopsy. The lymph node specimen contains several portions of lymph nodes with intact capsule. The architecture is generally intact with focal effacement seen. Prominent pigment is seen within sinusoids. This most likely represents hemosiderin. The cells otherwise show a combination of lymphocytes and plasma cells, with scattered plasmablasts and large noncleaved cells scattered throughout. No viral inclusions are seen. Occasional cells contain hyperchromatic nuclei approaching those described for "atypical immunoblasts". No extension beyond the capsule of nodes is appreciated. Some residual follicles are noted. An EBER stain is performed. The stain is suboptimal in so far as the intensity of staining is light. However, scattered individual nuclei are positive. These cells number 1 to several in most high power fields. They constitute only a minority of cells. The second part consists of a renal allograft biopsy and is interpreted as using the kidney template:
(2 H&E, 1 PAS)
1. Glomerulosclerosis
1.1 Number of glomeruli . . .
. .(29 )
1.2 Number globally sclerotic . .(0 )
1.3 Segmental sclerosis . .
. . .( )YES(x )NO
2. Glomerulitis(g). . . . . . . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
3. Interstitial inflammation(i) . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
(check if
present) . . . . . . .( )Neutrophils( )Eosinophils
4. Intimal arteritis(v) . . . . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not
evaluable
5. Tubulitis(t) . . . . . . . . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
6. Arteriolar hyalin(ah). . . . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not
evaluable
Nodular form . . . . . . . . . . .( )YES(x )NO
7. Chronic glomerular change(cg). . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
7b. Mesangial
matrix increase (mm) . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
8. Interstitial fibrosis(ci). . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
9. Tubular
atrophy(ct). . . . . . . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
10. Vascular intimal sclerosis(cv) . .(x )0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not
evaluable
10b. Number of arteries with internal elastic lamina: (3 )
11. Other findings:
Focal calcification is seen. Mild tubular dilatation
with granular debris within tubular lumens is noted.
12. Diagnostic categories (Check as many categories as appropriate)
(
)KDARO: Normal
( )KDAB: Antibody mediated rejection
( )KDARB: Borderline
change (i0-2, t0-2, v0)
( ) Acute rejection (specify g, i, t, v grades):
(
)KDAR1A: Banff Type 1A (i1-3, t2, v0)
( )KDAR1B: Banff Type 1B (i2-3, t3,
v0)
( )KDAR2A: Banff Type IIA (i1-3, t0-3, v1)
( )KDAR2B: Type 2B (i1-3,
t0-3, v2)
( )KDAR3: Type III (i1-3, t0-3, v3)
( ) Chronic allograft
nephropathy (Specify cg, ci, ct, cv grades):
( )KDCR1a: Mild, without
specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR1b: Mild, with specific
changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR2a: Moderate, without specific
changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR2b: Moderate, with specific
changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR3a: Severe, without specific
changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR3b: Severe, with specific changes
suggesting chronic rejection
( ) KDDR: Tubular and/or myocyte vacuolization
c/w drug-associated changes.
( ) KDAT: Acute tubular necrosis.
( ) KDDO:
Donor disease.
Other:
( ) Recurrent disease (specify)
( ) Subcapsular
injury ( )Pyelonephritis
( ) CMV ( )PTLD
( ) Obstruction ( )Reflux
( )
Vascular thrombosis (specify)
(x ) Miscellaneous Recovery from probable prior
tubular injury.
The morphologic changes in the lymph nodes, together with the occasional EBER positive cells, suggest that the process reflects a reactive lymphadenitis with focal features compatible with a form of PTLD referred to as plasma cell hyperplasia. Both of these processes are considered to be hyperplasias.