Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None
TPIS Related Resources:
Neoplasia
Transplant Topics
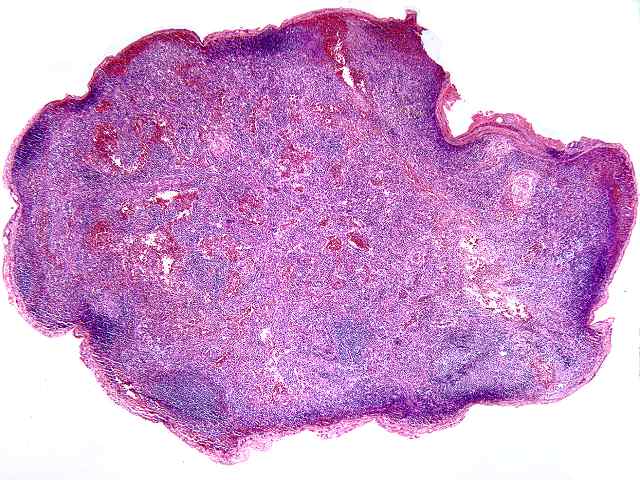
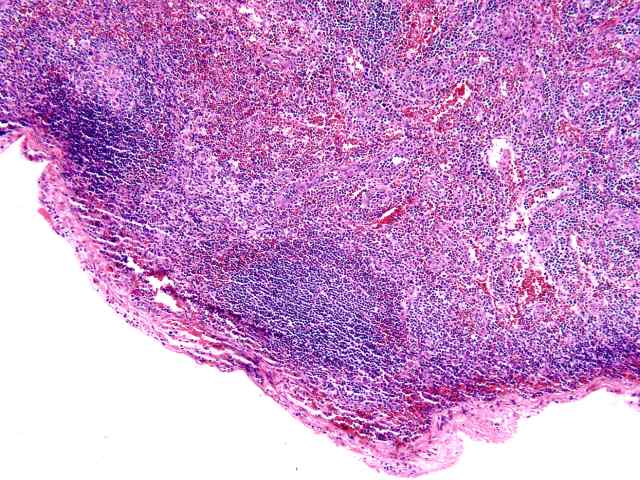
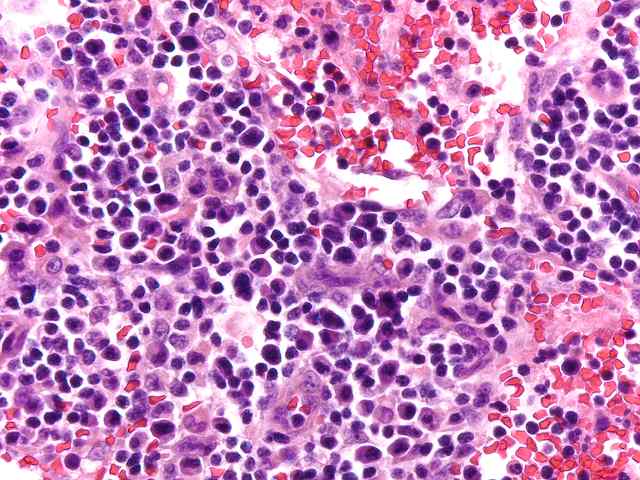
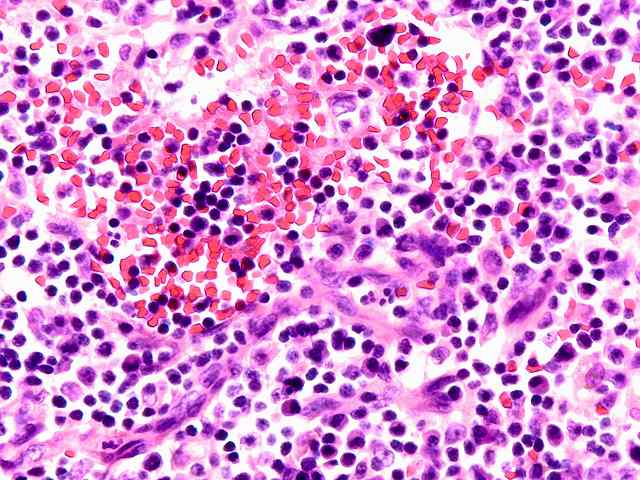
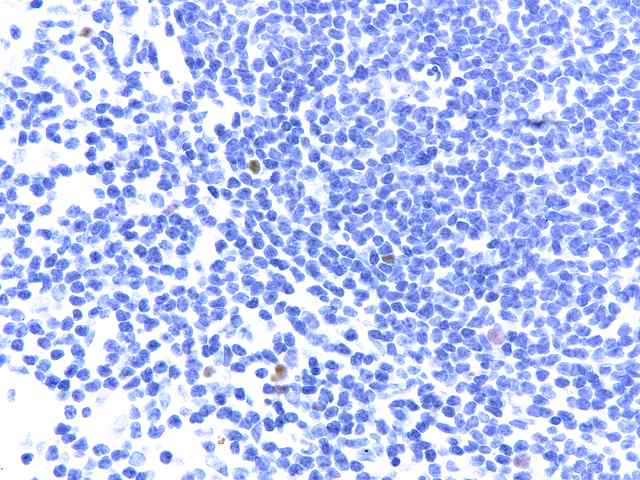
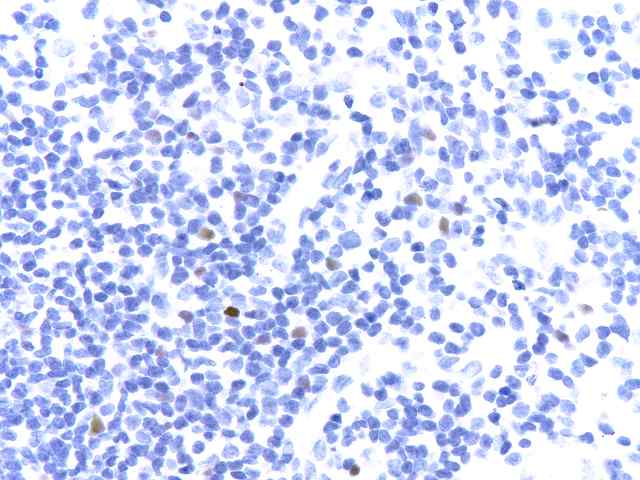
The specimen consists of two samples of lymph nodes, A1 and D1. Slide A1 contains two portions of tissue with a small amount of lymph node present. Occasional primary follicles including several with mildly atrophic germinal centers are seen. Elsewhere, a more diffuse proliferation of normal appearing lymphoid and plasma cell elements are seen in a background of small vessel hyperplasia. The cells contain moderate numbers of mature plasma cells, including some large binucleated forms. No evidence of tumor is seen. No destruction of underlying architecture is noted. An EBER stain is performed and shows occasional scattered positive cells ranging in numbers from one to several per high power microscopic field.
A similar appearance is seen on the lymph node section in Slide D1. Here however there appears to be a slightly more prominent diffuse component in the background of vascular hyperplasia. Again, mixed mononuclear elements, including substantial numbers of plasma cells, are seen. Scattered neutrophils are seen within the vessels. The EBER stain shows similar results, exhibiting scattered positive cells in a distinct minority.
Small numbers of EBER positive cells are seen in both node specimens. The appearance is that of a reactive condition. No evidence of neoplastic PTLD is appreciated. The process ranges from a benign low grade EBV lymphadenitis to one that has been described as plasma cell hyperplasia, also associated with EBV. The difference between these two histologic conditions is not well defined, and both may be considered as hyperplastic responses related to EBV infection.