 Contributed by Parmjeet S. Randhawa, M.D.
Contributed by Parmjeet S. Randhawa, M.D.
PATIENT HISTORY:
Per referral letter, the patient is a 13-year-old male who has
had a history of cough and recurrent chest infections since early
childhood. A clinical diagnosis of generalized bronchiectasis
was made last year. Following high resolution CT scanning, the
radiologist suggested a diagnosis of diffuse panbronchiolitis.
There is no history of asthma-like attacks. He was admitted
recently for thoracotomy. A right middle lobectomy was
performed. The right upper and lower lobes (abnormal on CT) were
reported to be normal on inspection and palpation. Wedge
biopsies taken of each of these lobes were unremarkable. The
right middle lobe received was firm, contracted and covered with
fibrin exudate. Cut sections showed ectatic bronchi close
together with scattered yellow foci. Histology does not show
typical features of bronchiolitis, and in view of the patient's
age and the rarity of this condition outside Japan, we are not
sure if this diagnosis can be made. Review of outside material.
Final Diagnosis (Case 4)
LUNG, RIGHT MIDDLE LOBE, LOBECTOMY -
- SEVERE BRONCHIECTASIS.
- CHANGES OF PULMONARY ARTERY HYPERTENSION WITH DILATATION
LESIONS AND FOCAL INFARCTION.
Comment:
Diffuse panbronchiolitis typically does not invlove cartilaginous B
bronchi or cause disease limited to a single lobe of the lung.
Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None
TPIS Related Resources:
None.
Gross Description (Case )
The specimen consists of four (4) consult slides. No surgical pathology report is received with the specimen.
Microscopic Description (Case 4)
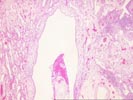
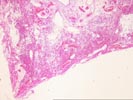
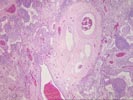
Sections of the right middle lobe show severe bronchiectasis. The
bronchi and bronchioles are dilated, and contain acute and
chronic inflammatory cells,foamy histiocytes and hypertrophic
Type II pneumocytes. The bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue
shows marked hyperplasia with numerous active germinal centers.
Wedge-shaped subpleural infarcts are present; the underlying
pulmonary arteries show intimal thickening and medial
hypertrophy, but no thrombosis. Section 1A shows a pulmonary
artery surrounded by dilated venous channels, consistent with a
dilatation lesion. One focus of bronchial ossification and
extramedullary hematopoiesis is noted. The alveolar septae are
thickened and show focal honeycomb change. There are occasional
multinucleate giant cells containing prominent nucleoli, but no
definite viral inclusions.
Please mail comments, corrections or suggestions to the
TPIS administration at the UPMC.


