PRE-OP DIAGNOSIS: ?chronic hepatitis C.
POST-OP DIAGNOSIS: Not
given.
PROCEDURE: Liver biopsy.
Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None
TPIS Related Resources:
Liver
Transplant Topics
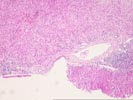
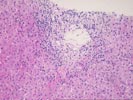
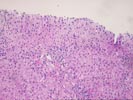
The liver biopsy shows generally normal lobular landmarks, but the portal tracts are expanded and fibrotic and, in a few areas, portal-based fibrous bridges have begun to appear. The portal tracts contain a moderate mononuclear infiltrate composed primarily of lymphocytes (with lymphoid aggregates) and occasional plasma cells and a rare scattered eosinophil and neutrophil. Focal minor ductular proliferation is identified. Piecemeal necrosis is patchy but is of moderate degree in some areas. Intralobular bile ducts are intact, with no florid duct lesions or granulomas identified. The lobules demonstrate minimal macrovesicular steatosis and a mild to moderate lobular inflammatory infiltrate accompanied by numerous focal necroses and occasional acidophilic bodies. No ground glass hepatocytes, viral inclusions, pigment deposition, cytoplasmic globules or steatohepatitis is seen.
Overall the changes are those of a moderately active chronic hepatitis with features compatible with hepatitis C positivity.
| KNODELL'S HISTOLOGY ACTIVITY INDEX | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | RANGE | SCORE |
| Periportal and bridging necrosis | (0-10) | 3 |
| Intralobular degeneration and necrosis | (0-4) | 3 |
| Portal inflammation | (0-4) | 3 |
| Fibrosis | (0-4) | 1-3 |
| TOTAL | (0-22) | 10-13/22 |
The numerical scoring system of histologic activity index (HAI) has been developed to grade the liver biopsies of chronic active hepatitis. This is based on four categories of periportal and bridging necrosis, intralobular degeneration and necrosis, portal inflammation and fibrosis, with total score of up to 22. This scoring system is correlated well with the severity of disease. A copy of the original paper published by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease [Hepatology 1:431, 1981] is available at the Department of Pathology upon request.