Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None
TPIS Related Resources:
Modified HAI Grading
Liver Transplant Topics
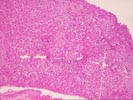
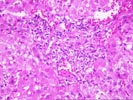
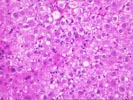
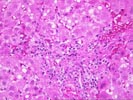
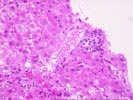
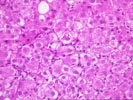
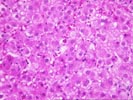
(1 HE, 1 Trichrome, 1 Iron) The biopsy is small and fragmented. In most regions the normal lobular architecture appears intact, but slightly distorted because of mild portal expansion and vague intralobular regenerative changes. A few of the portal tracts show mild fibrosis and contain a mild mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate. Bile ducts are intact. Throughout the lobules, there is moderate to severe lobular disarray, Kupffer cell hypertrophy, mild mixed steatosis, numerous acidophilic bodies and hepatocellular swelling with regeneration. Several hepatocytes contain Mallory's-like hyaline. However, no significant lobular neutrophilia or steatotic degeneration of hepatocytes are seen. No viral inclusions, prominent pigment deposition or ground glass cells are seen. The prominent lobular component including hepatocellular swelling, spotty hepatocyte necrosis and focal Mallory's-like hyaline and the cholestatic liver injury tests suggest an acute or active lobular hepatitis, with a cholestatic component. Considering the patient history, the changes are most likely related viral hepatitis, type C. However, other and/or co- existent potential insults, such as drug or alcohol, should be excluded. The clinical history relates the presence of anti-HCV antibodies. Confirmation of HCV infection by PCR analysis may be helpful. Although the duration of hepatitis C virus infection is unknown, the clinical history relates chronic disease. Therefore, the modified hepatitis activity index will be applied. In addition, the trichrome stain reveals mild to focally mild portal fibrosis with focal regenerative change. Application of the modified HAI category is as follows: Application of the modified hepatitis activity index is as follows:
| MODIFIED HEPATITIS ACTIVITY INDEX | ||
|---|---|---|
| GRADING | RANGE | SCORE |
| Periportal or periseptal interface hepatitis (piecemeal necrosis) | (0-4) | 1 |
| Confluent necrosis | (0-6) | 0 |
| Focal (spotty) lytic necrosis, apoptosis and focal inflammation | (0-4) | 3 |
| Portal inflammation | (0-4) | 1 |
| TOTAL | (0-18) | 5 |
| STAGING | RANGE | SCORE |
| Fibrosis | (0-6) | 1 |