 Contributed by
Anthony J. Demetris, M.D.
Contributed by
Anthony J. Demetris, M.D.
PATIENT HISTORY: Per referral report, the patient is an elderly male
with elevated alpha fetoprotein. The patient was admitted to the hospital following outpatient workup which revealed the presence of a right
proximal, third clavicular, lytic lesion in his bone and also a probable hepatic
metastasis. This elderly male presented with some ecchymosis of the right
clavicle about five weeks ago. X-ray revealed the presence of lytic lesion.
Following this out patient workup was continued to include lab work, CT scan of
the chest, abdomen and pelvis. These workups failed to reveal any significant
primary tumor. However, there was evidence of probably metastatic infiltration
of the liver. The patient has a positive history of having COPD in the past. He
still smokes one half to one pack of cigarettes per day. He was a former
drinker. He has been drinking some wine lately but not very much according to
his daughter, may an occasional glass with Sunday dinner and other than that, he
has abstained totally from alcohol. His current medical regimen includes
Glucotrol 5 mg po daily; Lasix 40 mg daily and Aldactone 25 mg bid. He has
allergies to Penicillin. R/O hepatoma/liver metastasis. Review of outside
material.
Final Diagnosis (Case 36)
LIVER, NEEDLE BIOPSY -
- WELL DIFFERENTIATED HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA.
- FOCAL FIBROSIS, SUGGESTIVE OF UNDERLYING CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE (see
microscopic description).
Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None
TPIS Related Resources:
National
Cancer Institute PDQ treatment information on liver cancer
Liver
Transplant Topics
Gross Description - Case 36
The specimen consists of one (1) consult
slide and one (1) paraffin block with an accompanying surgical pathology report.
Microscopic Description - Case 36
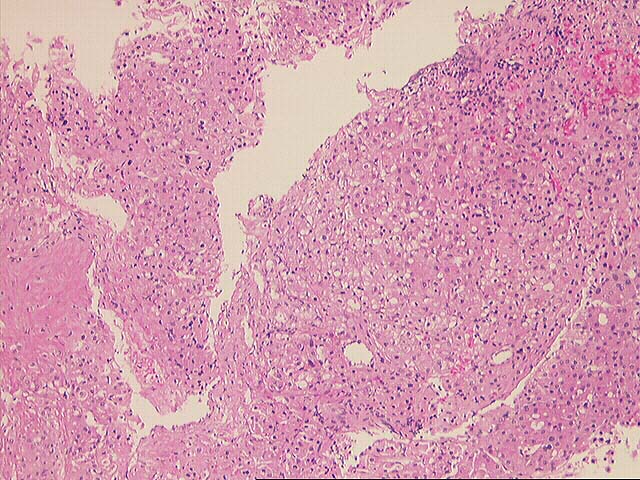
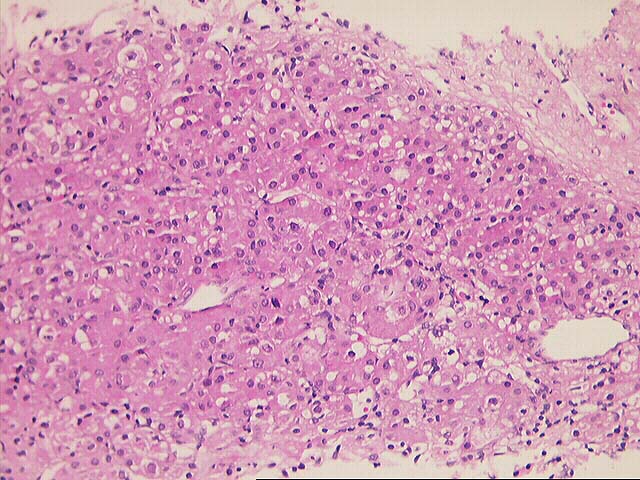
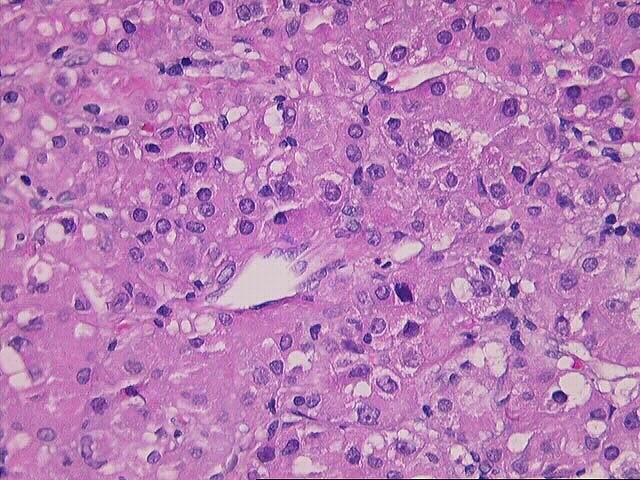
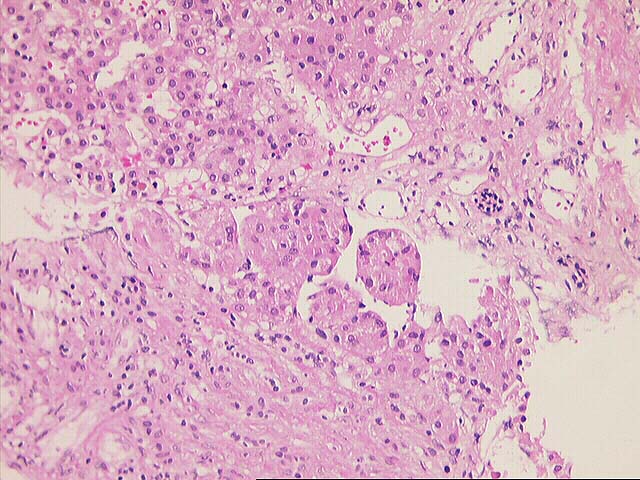
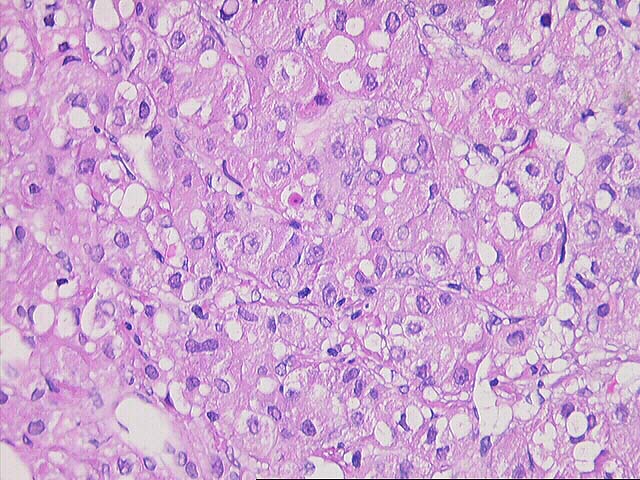
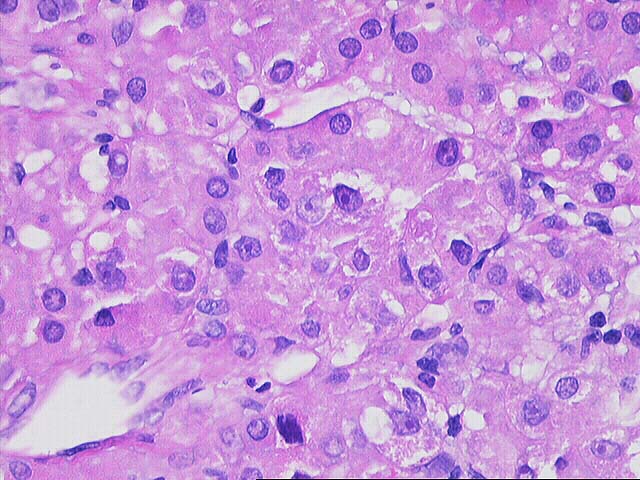
The specimen consists of multiple fragmented needle cores of liver. No normal
hepatic architecture is identified. Instead, the tissue consists of a few areas
of fibrous septae containing bile ducts and other fibrous tracts intermixed with
hepatocytes growing in a macrotrabecular growth pattern. No normal sinusoidal
architecture is identified. Instead, the trabeculae are greater than five to six
cell layers thick in some areas. In addition, there are aberrant vessels
intermixed within the hepatocytes. Cytologically, the neoplastic cells contain
an increased nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio, an irregular nuclear membrane, prominent
eosinophilic nucleoli and focal bile production is seen. Mallory's-like hyaline
is also focally present.
Overall, the histopathological changes are most consistent with a well
differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma. This contention is based on the overall
architectural pattern of growth, combined with the presence of "aberrant"
vessels and cytological characteristics of the cells.
Finally, most of the needle core consists of neoplastic tissue and the
limited remaining hepatic parenchyma is inadequate to definitively assess for
the presence of underlying liver disease. However, the focal fibrosis is
suggestive of chronic liver injury and fibrosis.
Please mail comments, corrections or suggestions to the TPIS administration at the
UPMC.





