COMMENT:
The histopathologic appearances are non-specific, but do not
exclude the possibility of autoimmune hepatitis. A definitive
clinical diagnosis should be based on exclusion of viral etiology
and presence of autoimmune markers.
In view of the presence of focal steatosis and sinusoidal
fibrosis, consideration should also be given to hepatic injury
associated with ethanol use, diabetes and obesity.
Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
NONE
TPIS Related Resources:
Knodell Scoring
Liver Transplant Topics
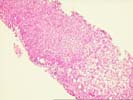
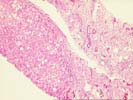
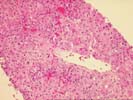
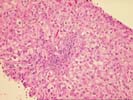
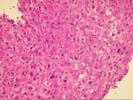
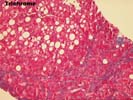
The architecture of the liver is completely replaced by a mixed cirrhosis. The fibrous tissue septae separating the nodules contain an active mononuclear infiltrate in which occasional plasma cells are present. The lobule shows focal macrovesicular steatosis, mild swelling, regenerative changes and evidence of hepatocyte injury. No viral inclusions, granulomas, duct lesions, duct loss, or Mallory's hyaline are noted. The central veins show no significant pathologic change. The trichrome reveals the presence of focal sinusoidal fibrosis. The Knodell score is assigned as follows:
| KNODELL'S HISTOLOGY ACTIVITY INDEX | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | RANGE | SCORE |
| Periportal and bridging necrosis | (0-10) | 3 |
| Intralobular degeneration and necrosis | (0-4) | 2 |
| Portal inflammation | (0-4) | 3 |
| Fibrosis | (0-4) | 4 |
| TOTAL | (0-22) | 12 |
The numerical scoring system of histological activity index (HAI) has been developed to grade the liver biopsies of chronic active hepatitis. This is based on four categories of periportal and bridging necrosis, intralobular degeneration and necrosis, portal inflammation and fibrosis, with total score of up to 22. This scoring system is correlated well with the severity of disease. A copy of the original paper published by American Association for the Study of Liver Disease [Hepatology 1:431-435 (1981)] is available at the Department of Pathology upon request.