Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
NONE
TPIS Related Resources:
National Cancer Institute PDQ treatment information on liver cancer
Liver Transplant Topics
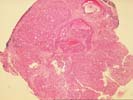
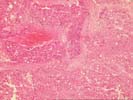
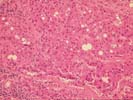
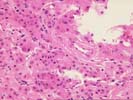
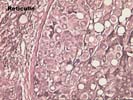

The sections show subcapsular hepatic tissue containing large nests of hepatocytes separated by dense and sometimes lamellar fibrous stroma. These nests abut directly on the fibrous septa without intervening cholangioles, and this feature tends to exclude both regenerative nodules as seen in cirrhosis and focal nodular hyperplasia. In addition, several aberrant arteries are present, and this is generally an indication of neoplastic hepatocyte proliferations. The hepatocytes contain mild macrovesicular steatosis and demonstrate mild cytologic atypia with occasional irregular and hyperchromatic nucleir, although many cells contain round to oval nuclei with modest nucleoli. No mitoses or vascular invasion is seen. Occasional cells also contain pale areas within the cytoplasm that suggest the pale bodies of fibrolamellar carcinoma; the nuclear features, however, do not support this diagnosis. There is no adjacent liver present to assess for a background cirrhosis.
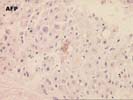
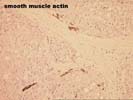
Several special stains were performed to further characterize this lesion. The reticulin stains shows focal loss of reticulin staining with other areas showing course irregular deposition. The CD34 stain demonstrates positive endothelial staining throughout many of the cellular nests; although this is nonspecific, it is a feature typical of hepatocellular carcinoma. The smooth muscle actin stain confirms the presence of aberrant arteries. The alpha-fetoprotein stain is largely negative although one cell with equivocal cytoplasmic staining is noted.
This is a challenging case, but overall the features support a diagnosis of low-grade hepatocellular carcinoma. Despite the mild cytologic features, the architectural alterations are beyond what can be considered a benign regenerative or hyperplastic process. Additional information provided by radiographic imaging, the observations at laparoscopy, and serum studies of alpha-fetoprotein and hepatitis serology would be helpful, and should be correlated with the histologic findings.