Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
NONE
TPIS Related Resources:
Liver
Allograft Biopsy Rejection Criteria
Liver
Transplant Topics
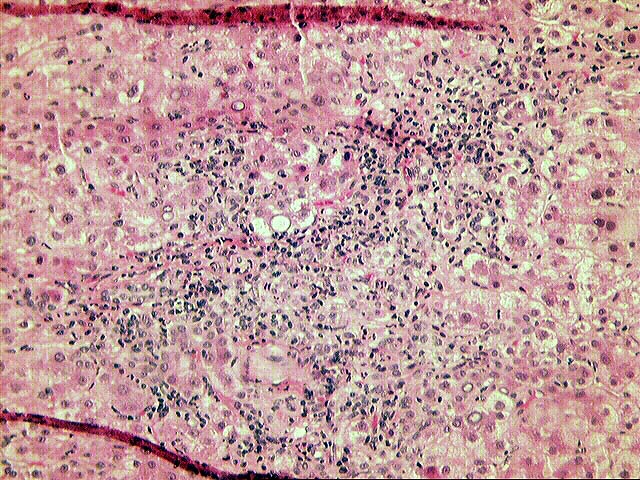
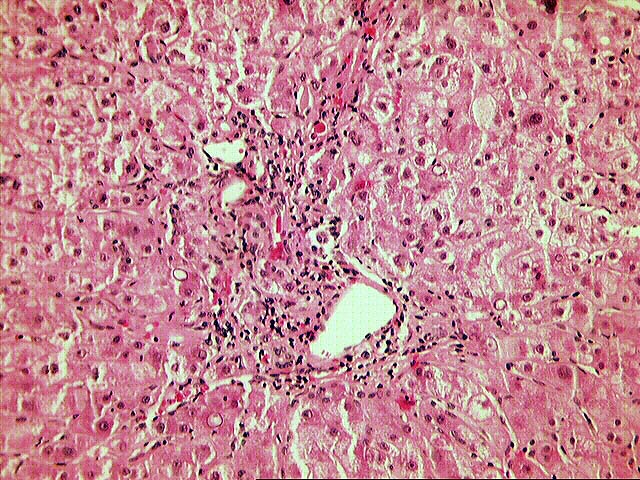
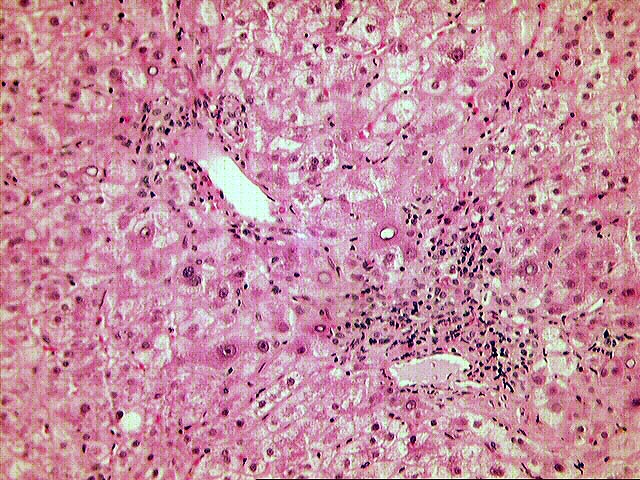
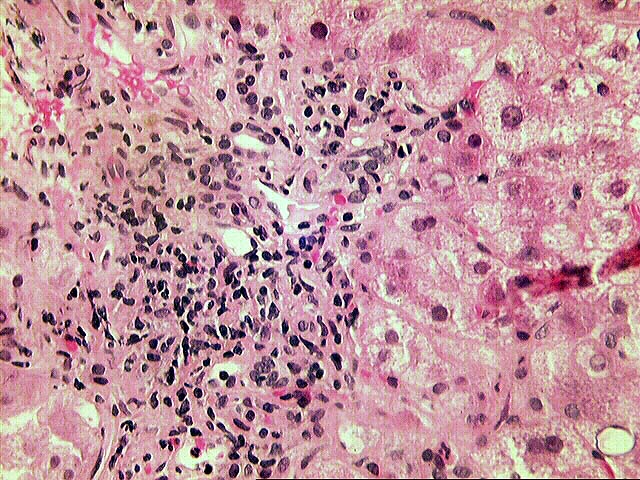
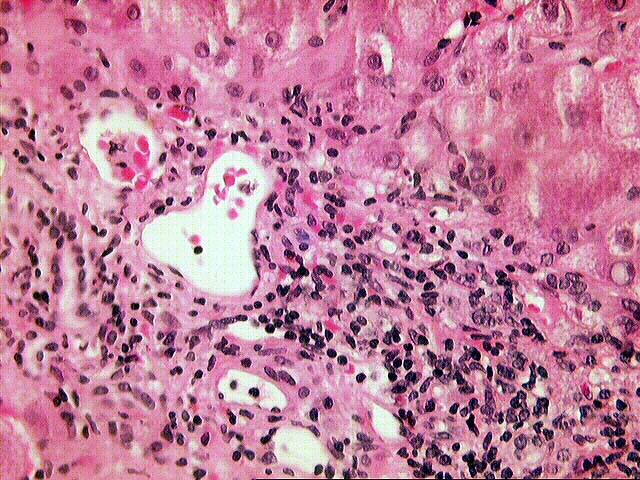
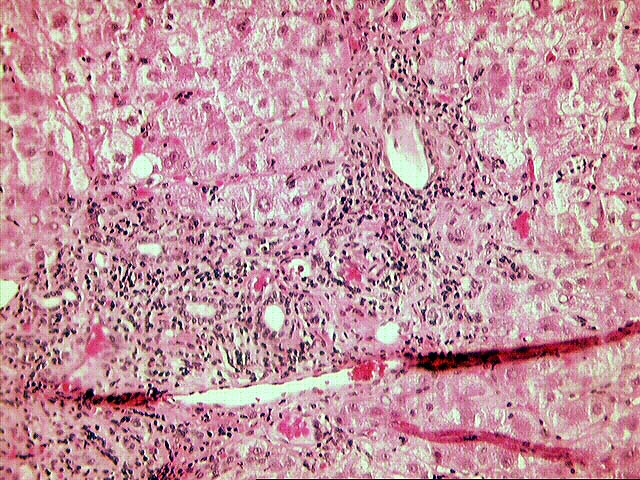
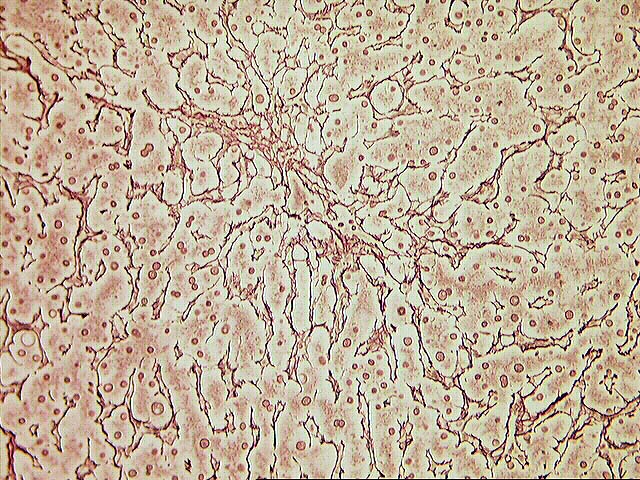
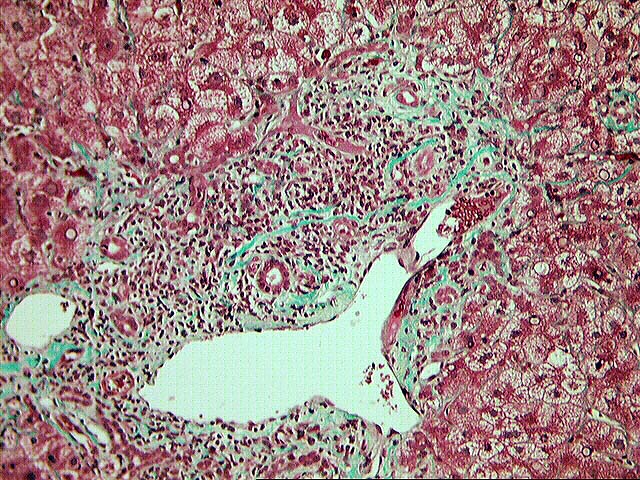
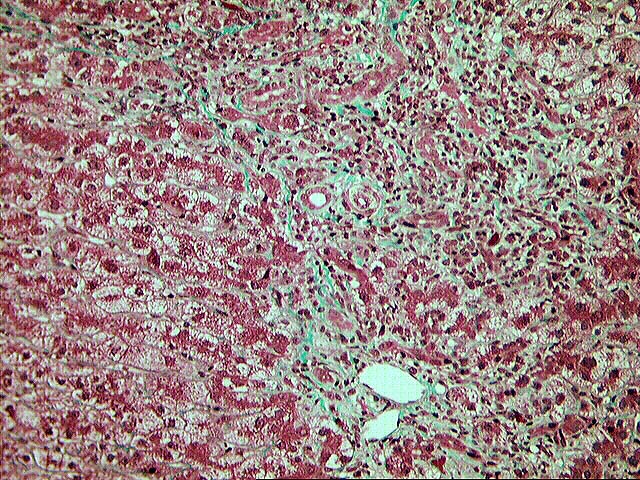
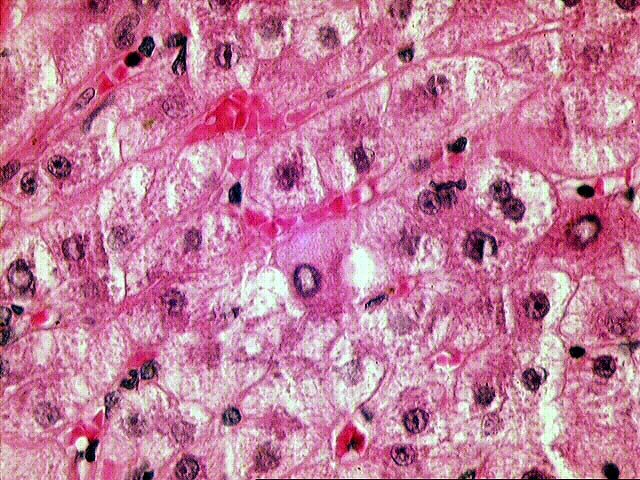
The normal lobular architecture is distorted by mild to moderate portal expansion with focal portal-to-portal and portal-to- central bridging fibrosis. On closer examination, the portal tracts contain a mild to focally moderate mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate. Focal bile duct infiltration and damage are seen, but, in general, this change is not particularly widespread, and many normal-appearing ducts are present. Instead, there is prominent interface activity with cholangiolar reactivity. Throughout the lobule, there is moderate disarray, Kupffer cell hypertrophy, hepatocellular swelling, ground glass hepatocytes and occasional acidophilic bodies. Application of the Knodell scoring system is as follows:
| KNODELL'S HISTOLOGY ACTIVITY INDEX | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | RANGE | SCORE |
| Periportal and bridging necrosis | (0-10) | 3 |
| Intralobular degeneration and necrosis | (0-4) | 1 |
| Portal inflammation | (0-4) | 3 |
| Fibrosis | (0-4) | 1-3 |
| TOTAL | (0-22) | 8-10 |
The numerical scoring system of histologic activity index (HAI) has been developed to grade the liver biopsies of chronic active hepatitis. This is based on four categories of periportal and bridging necrosis, intralobular degeneration and necrosis, portal inflammation and fibrosis, with total score of up to 22. This scoring system is correlated well with the severity of disease. A copy of the original paper published by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease [Hepatology 1:431, 1981] is available at the Department of Pathology upon request.
Overall, the changes at this time, are indicative of an active chronic hepatitis, viral type B, because of the ground glass cells and previously positive immunostains for HBV antigens. Although it is difficult to determine the extent to which acute rejection is contributing to the process, most of the inflammation is located near and directed at the interface zone. Thus, it is my opinion that chronic hepatitis is the predominant process and rejection is a minor factor. However, any marked increase of gamma glutamyltranspeptidase and/or alkaline phosphatase should arouse a suspicion of rejection and re- evaluation may be needed.