Comment: The interstitial inflammation & tubulitis is most consistent with mild acute cellular rejection (Banff 97, Type 1A). A short course of steroids would be a reasonable option to try, if there are no other contraindications for such therapy.
Atypical tubular nuclei raised concern for polyoma virus infection, but this could not be substantiated by immunohistochemistry or in-situ hybridization, performed after destaining of H&E sections. No tissue remains in the paraffin block for further studies. Continued clinical monitoring is suggested. The urine can be serially examined for the presence of viral inclusions. Should a repeat biopsy be clinically indicated, we would like to repeat immunohistochemistry for viral antigens.
Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
None.
TPIS Related Resources:
Kidney Transplant Topics
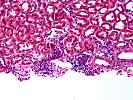
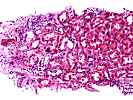
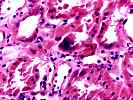
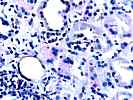
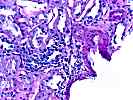
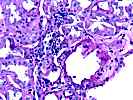
1. Glomerulosclerosis
1.1 Number of glomeruli . . . . .(18)
1.2 Number globally sclerotic . .(5)
1.3 Segmental sclerosis . . . . .( )YES(X)NO
2. Glomerulitis(g). . . . . . . . . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
3. Interstitial inflammation(i) . . .( )0 ( )1 (X)2 ( )3
(check if present) . . . . . . .( )Neutrophils( )Eosinophils
4. Intimal arteritis(v) . . . . . . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not evaluable
5. Tubulitis(t) . . . . . . . . . . .( )0 ( )1 (X)2 ( )3
6. Arteriolar hyalin(ah). . . . . . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not evaluable
Nodular form . . . . . . . . . . .( )YES( )NO
7. Chronic glomerular change(cg). . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
7b. Mesangial matrix increase (mm) . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
8. Interstitial fibrosis(ci). . . . .( )0 ( )1 (X)2 ( )3
9. Tubular atrophy(ct). . . . . . . .( )0 ( )1 (X)2 ( )3
10. Vascular intimal sclerosis(cv) . .(X)0 ( )1 ( )2 ( )3
( )Not evaluable
10b. Number of arteries with internal elastic lamina: (2)
11. Other findings:
Tubular multinucleation, hyperchromasia, and flattening of nuclei; discrete viral inclusions not seen; sv40 stain questinable weak stain in single tubule; in-situ hybridization for BK virus ve; interstitial calcifications.
12. Diagnostic categories (Check as many categories as appropriate)
( )KDARO: Normal
( )KDAB: Antibody mediated rejection
( )KDARB: Borderline change (i0-2, t0-2, v0)
(X) Acute rejection (specify g, i, t, v grades):
(X)KDAR1A: Banff Type 1A (i1-3, t2, v0)
( )KDAR1B: Banff Type 1B (i2-3, t3, v0)
( )KDAR2A: Banff Type IIA (i1-3, t0-3, v1)
( )KDAR2B: Type 2B (i1-3, t0-3, v2)
( )KDAR3: Type III (i1-3, t0-3, v3)
(X) Chronic allograft nephropathy (Specify cg, ci, ct, cv grades):
( )KDCR1a: Mild, without specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR1b: Mild, with specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
(X)KDCR2a: Moderate, without specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR2b: Moderate, with specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR3a: Severe, without specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( )KDCR3b: Severe, with specific changes suggesting chronic rejection
( ) KDDR: Tubular and/or myocyte vacuolization c/w drug-associated changes.
( ) KDAT: Acute tubular necrosis.
( ) KDDO: Donor disease.
Other:
( ) Recurrent disease (specify)
( ) Subcapsular injury (X)Pyelonephritis
( ) CMV ( )PTLD
( ) Obstruction ( )Reflux
( ) Vascular thrombosis (specify)
(X) Miscellaneous