Previous Biopsies on this Patient:
NONE
TPIS Related Resources:
Liver Allograft Rejection Grading
Liver Transplant Topics
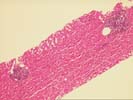
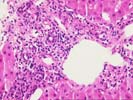
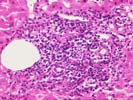
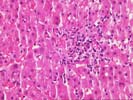
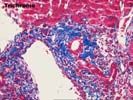
The normal lobular architecture is distorted by mild portal expansion because of a mild to moderate mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate, which is focally arranged into nodular aggregates. Despite the portal inflammation, mild bile duct damage is only focally seen and many other ducts are normal in appearance. Moreover, some of the portal inflammation spills over into the edge of the lobules where there is mild ongoing interface activity.
Throughout the lobules, there is mild Kupffer cell hypertrophy and occasional acidophilic bodies. There is also a slight increase in sinusoidal inflammatory cells, but no viral inclusions nor ground glass cells are seen. No significant increase in hepatic iron stores are identified. The trichrome stain reveals mild to moderate portal fibrosis, but the normal spatial relationship between portal tracts and central veins is maintained in most areas.
Overall, the histopathological changes are most consistent with clinical history of recurrent Type C viral hepatitis. The rejection activity, at present, is minimal to absent. This contention is based on the patchy nature of the inflammatory infiltrate combined with the focality of the duct damage, the lack of portal or central venulitis and the presence of mild interface and lobular activity. Application of the Knodell scoring system is as follows:
| KNODELL'S HISTOLOGY ACTIVITY INDEX | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | RANGE | SCORE |
| Periportal and bridging necrosis | (0-10) | 1-3 |
| Intralobular degeneration and necrosis | (0-4) | 1 |
| Portal inflammation | (0-4) | 3 |
| Fibrosis | (0-4) | 1-3 |
| TOTAL | (0-22) | 6-10 |
The numerical scoring system of histologic activity index (HAI) has been developed to grade the liver biopsies of chronic active hepatitis. This is based on four categories of periportal and bridging necrosis, intralobular degeneration and necrosis, portal inflammation and fibrosis, with total score of up to 22. This scoring system is correlated well with the severity of disease. A copy of the original paper published by the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease [Hepatology 1:431, 1981] is available at the Department of Pathology upon request.